How to add an external cluster to ArgoCD to manage it ¶
Goal ¶
Given an ArgoCD installation created with binbash Leverage Landing Zone using the EKS layer, add and manage an external Cluster.
There can be a single ArgoCD instance for all cluster or multiple instances installed:
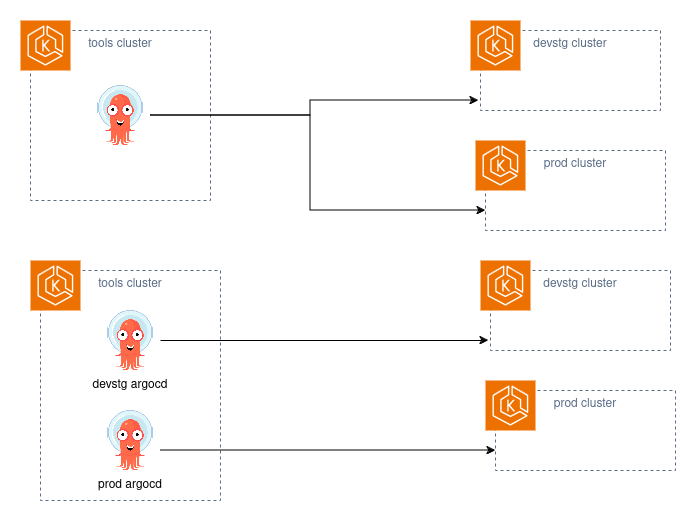
Warning
If two or more cluster wide ArgoCD instances will be deployed in the same cluster, please see these notes!!!!
Assumptions ¶
We are assuming the binbash Leverage Landing Zone is deployed, two accounts called shared and apps-devstg were created and a region us-east-1 is being used. In any case you can adapt these examples to other scenarios.
Requirements ¶
The target cluster must have IRSA enabled.
If this cluster was created using the binbash Leverage Landing Zone EKS layer this req is met.
Also the VPC for both K8s cluster should be connected. (e.g. VPCPeerings have to be in place between them)
Info
Learn how to create VPCPeerings using binbash Leverage Landing Zone here.
How to ¶
There are a few ways to accomplish this. Here are two of them, you can find more here.
- IAM Roles
- Bearer tokens
IAM Roles ¶
First we need to understand the how-to do this.
Given this diagram:
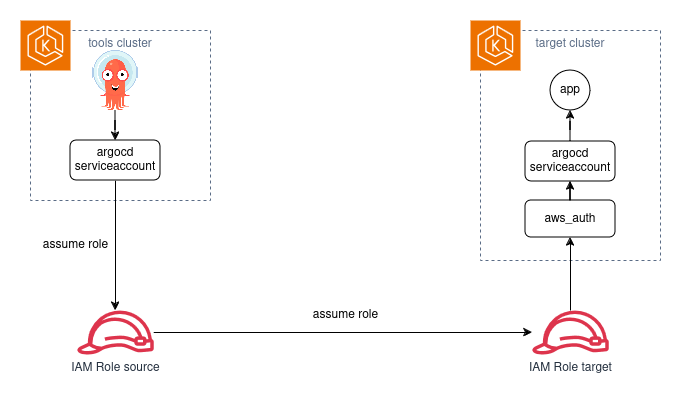
this workflow shows up:
- ArgoCD deployment, in Kubernetes, has a ServiceAccount
- this ServiceAccount is bound to an IAM Role that we'll call source
- the source Role can assume a second Role that we'll call target
- the target Role can assume RBAC permissions using the
aws_authconfig map in the target cluster
This way, ArgoCD, from the source cluster, can deploy stuff into the target cluster.
Steps ¶
These steps were created to match two EKS clusters, in two AWS accounts, created using binbash Leverage Landing Zone.
ArgoCD will be deployed in shared account and will be controlling the cluster in apps-devstg.
Info
- source account:
shared - target account:
apps-devstg
Create the source identities ¶
Info
This has to be done in shared account.
ArgoCD should be deployed using the shared/us-east-1/k8s-eks/k8s-components layer.
The identities to be used by ArgoCD have to be updated in the shared/us-east-1/k8s-eks/identities layer.
So, go into this layer and edit the ids_argocd.tf file.
Here the ServiceAccount used have to be modified to include all the possibilities in the argocd namespace:
module "role_argocd_devstg" {
source = "github.com/binbashar/terraform-aws-iam.git//modules/iam-assumable-role-with-oidc?ref=v5.37.1"
create_role = true
role_name = "${local.environment}-argocd-devstg"
provider_url = replace(data.terraform_remote_state.eks-cluster.outputs.cluster_oidc_issuer_url, "https://", "")
role_policy_arns = [aws_iam_policy.argocd_devstg.arn]
oidc_fully_qualified_subjects = ["system:serviceaccount:argocd-devstg:*"]
tags = local.tags_cluster_autoscaler
}
Note all the argocd namespace's ServiceAccounts were added to oidc_fully_qualified_subjects (because different ArgoCD components use different SAs), and they will be capable of assume the role ${local.environment}-argocd-devstg. (Since we are working in shared the role will be shared-argocd-devstg)
This role lives in shared account.
Apply the layer:
leverage tf apply
Info
Note this step creates a role and binds it to the in-cluster serviceaccounts.
Create the target role and change the aws_auth config map ¶
Info
This has to be done in apps-devstg account.
Create the role ¶
Go into the apps-devstg/global/base-identities layer.
In file roles.tf add this resource:
module "iam_assumable_role_argocd" {
source = "github.com/binbashar/terraform-aws-iam.git//modules/iam-assumable-role?ref=v4.1.0"
trusted_role_arns = [
"arn:aws:iam::${var.accounts.shared.id}:root"
]
create_role = true
role_name = "ArgoCD"
role_path = "/"
#
# MFA setup
#
role_requires_mfa = false
mfa_age = 43200 # Maximum CLI/API session duration in seconds between 3600 and 43200
max_session_duration = 3600 # Max age of valid MFA (in seconds) for roles which require MFA
custom_role_policy_arns = [
]
tags = local.tags
}
Note MFA is deactivated since this is a programmatic access role. Also no policies are added since we need to assume it just to access the cluster.
Apply the layer:
leverage tf apply
Info
This step will add a role that can be assumed from the shared account.
Update the aws_auth config map ¶
cd into layer apps-devstg/us-east-1/k8s-eks/cluster.
Edit file locals.tf, under map_roles list add this:
{
rolearn = "arn:aws:iam::${var.accounts.apps-devstg.id}:role/ArgoCD"
username = "ArgoCD"
groups = ["system:masters"]
},
You can narrow the access modifying groups as per your own needs.
Apply the layer:
leverage tf apply
To recover the the API Server run this:
APISERVER=$(leverage kubectl config view --minify -o jsonpath='{.clusters[0].cluster.server}' | sed -E '/^\[/d')
Info
This step will add the role-k8sgroup binding.
Create the external cluster in ArgoCD ¶
Info
This has to be done in shared account.
In shared/us-east-1/k8s-eks/k8s-components layer modify files cicd-argocd.tf and chart-values/argocd.yaml and add this to the first one:
##------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## ArgoCD DEVSTG: GitOps + CD
##------------------------------------------------------------------------------
resource "helm_release" "argocd_devstg" {
count = var.enable_argocd_devstg ? 1 : 0
name = "argocd-devstg"
namespace = kubernetes_namespace.argocd_devstg[0].id
repository = "https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm"
chart = "argo-cd"
version = "6.7.3"
values = [
templatefile("chart-values/argocd.yaml", {
argoHost = "argocd-devstg.${local.environment}.${local.private_base_domain}"
ingressClass = local.private_ingress_class
clusterIssuer = local.clusterissuer
roleArn = data.terraform_remote_state.eks-identities.outputs.argocd_devstg_role_arn
remoteRoleARN = "role"
remoteClusterName = "clustername"
remoteServer = "remoteServer"
remoteName = "remoteName"
remoteClusterCertificate = "remoteClusterCertificate"
}),
# We are using a different approach here because it is very tricky to render
# properly the multi-line sshPrivateKey using 'templatefile' function
yamlencode({
configs = {
secret = {
argocd_devstgServerAdminPassword = data.sops_file.secrets.data["argocd_devstg.serverAdminPassword"]
}
# Grant Argocd_Devstg access to the infrastructure repo via private SSH key
repositories = {
webapp = {
name = "webapp"
project = "default"
sshPrivateKey = data.sops_file.secrets.data["argocd_devstg.webappRepoDeployKey"]
type = "git"
url = "git@github.com:VistaPath/webapp.git"
}
}
}
# Enable SSO via Github
server = {
config = {
url = "https://argocd_devstg.${local.environment}.${local.private_base_domain}"
"dex.config" = data.sops_file.secrets.data["argocd_devstg.dexConfig"]
}
}
})
]
}
Note these lines:
remoteRoleARN = "role"
remoteClusterName = "clustername"
remoteServer = "remoteServer"
remoteName = "remoteName"
remoteClusterCertificate = "remoteClusterCertificate"
Dictionary:
- remoteRoleARN: the role created in
apps-devstg(target) account - remoteClusterName: the target cluster name (e.g. "staging")
- remoteServer: the target cluster API URL
- remoteName: the target server name (the ARN)
- remoteClusterCertificate: the target cluster CA Certificate on Base64
And this in the second file:
configs:
clusterCredentials:
- name: ${remoteName}
server: ${remoteServer}
labels: {}
annotations: {}
namespaces: namespace1,namespace2
clusterResources: false
config:
awsAuthConfig:
clusterName: ${remoteClusterName}
roleARN: ${remoteRoleARN}
tlsClientConfig:
insecure: false
caData: ${remoteClusterCertificate}
clusterResources false is so that ArgoCD is prevented to manage cluster level resources.
namespaces scopes the namespaces on which ArgoCD can deploy resources.
Apply the layer:
leverage tf apply
Info
This step will create the external-cluster configuration for ArgoCD.
Now you can see the cluster in the ArgoCD web UI.
Bearer Tokens ¶
This is a simpler (than the previous one) method, but also is less secure.
It uses a bearer token, which should be rotated periodically. (maybe manually or with a custom process)
Given this diagram:
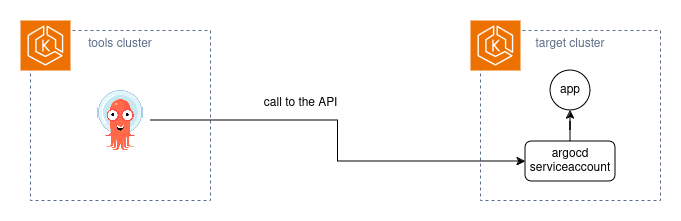
ArgoCD will call the target cluster directly using the bearer token as authentication.
So, these are the steps:
- create a ServiceAccount and its token in the target cluster
- create the external cluster in the source cluster's ArgoCD
Create the ServiceAccount ¶
Info
This has to be done in apps-devstg account.
There are two ways to grant access. Cluster level or namespace scoped.
If namespace scoped ServiceAccount, Role and Rolebinding are needed to grant access to ArgoCD to the target cluster. If cluster level then ServiceAccount, ClusterRole and ClusterRolebinding. The former needs the namespaces to be created beforehand. The later allows ArgoCD to create the namespaces.
In the target cluster identities layer at apps-devstg/us-east-1/k8s-eks/identities create a tf file and add this:
The following example is for namespace scoped way.
locals {
# namespaces ArgoCD has to manage
namespaces = toset(["test"])
}
provider kubernetes {
host = data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.endpoint
cluster_ca_certificate = base64decode(data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.certificate_authority.0.data)
token = data.aws_eks_cluster_auth.cluster.token
}
data "aws_eks_cluster" "cluster" {
name = data.terraform_remote_state.eks-cluster.outputs.cluster_name
}
data "aws_eks_cluster_auth" "cluster" {
name = data.terraform_remote_state.eks-cluster.outputs.cluster_name
}
resource "kubernetes_service_account" "argocd-managed" {
for_each = local.namespaces
metadata {
name = "argocd-managed"
namespace = each.key
}
}
resource "kubernetes_secret" "argocd-managed" {
for_each = local.namespaces
metadata {
annotations = {
"kubernetes.io/service-account.name" = kubernetes_service_account.argocd-managed[each.key].metadata.0.name
}
generate_name = "argocd-managed-"
namespace = each.key
}
type = "kubernetes.io/service-account-token"
wait_for_service_account_token = true
}
resource "kubernetes_role" "argocd-managed" {
for_each = local.namespaces
metadata {
name = "argocd-managed-role"
namespace = each.key
}
rule {
api_groups= ["*"]
resources= ["*"]
verbs= ["*"]
}
}
resource "kubernetes_role_binding" "argocd-managed" {
for_each = local.namespaces
metadata {
name = "${kubernetes_role.argocd-managed[each.key].metadata[0].name}-binding"
namespace = each.key
}
role_ref {
api_group = "rbac.authorization.k8s.io"
kind = "Role"
name = kubernetes_role.argocd-managed[each.key].metadata[0].name
}
subject {
kind = "ServiceAccount"
name = "argocd-managed"
namespace = each.key
}
}
The following example is for cluster level way.
provider kubernetes {
host = data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.endpoint
cluster_ca_certificate = base64decode(data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.certificate_authority.0.data)
token = data.aws_eks_cluster_auth.cluster.token
}
data "aws_eks_cluster" "cluster" {
name = data.terraform_remote_state.eks-cluster.outputs.cluster_name
}
data "aws_eks_cluster_auth" "cluster" {
name = data.terraform_remote_state.eks-cluster.outputs.cluster_name
}
resource "kubernetes_service_account" "argocd-managed" {
metadata {
name = "argocd-managed"
namespace = "kube-system"
}
}
resource "kubernetes_secret" "argocd-managed" {
metadata {
annotations = {
"kubernetes.io/service-account.name" = kubernetes_service_account.argocd-managed.metadata.0.name
}
generate_name = "argocd-managed-"
namespace = "kube-system"
}
type = "kubernetes.io/service-account-token"
wait_for_service_account_token = true
}
resource "kubernetes_cluster_role" "argocd-managed" {
metadata {
name = "argocd-managed-role"
}
rule {
api_groups= ["*"]
resources= ["*"]
verbs= ["*"]
}
}
resource "kubernetes_cluster_role_binding" "argocd-managed" {
metadata {
name = "${kubernetes_role.argocd-managed.metadata[0].name}-binding"
}
role_ref {
api_group = "rbac.authorization.k8s.io"
kind = "ClusterRole"
name = kubernetes_role.argocd-managed.metadata[0].name
}
subject {
kind = "ServiceAccount"
name = "argocd-managed"
namespace = "kube-system"
}
}
Info
This step will create a ServiceAccount, a Role with the needed permissions, the RoleBinding and the secret with the token. (or clusterrole and clusterrolebinding)
Also, multiple namespaces can be specified for namespace scoped way.
To recover the token and the API Server run this:
NAMESPACE=test
SECRET=$(leverage kubectl get secret -n ${NAMESPACE} -o jsonpath='{.items[?(@.metadata.generateName=="argocd-managed-")].metadata.name}' | sed -E '/^\[/d')
TOKEN=$(leverage kubectl get secret ${SECRET} -n ${NAMESPACE} -o jsonpath='{.data.token}' | sed -E '/^\[/d' | base64 --decode)
APISERVER=$(leverage kubectl config view --minify -o jsonpath='{.clusters[0].cluster.server}' | sed -E '/^\[/d')
Create the external cluster in ArgoCD ¶
Info
This has to be done in shared account.
In shared/us-east-1/k8s-eks/k8s-components layer modify files cicd-argocd.tf and chart-values/argocd.yaml and add this to the first one:
##------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## ArgoCD DEVSTG: GitOps + CD
##------------------------------------------------------------------------------
resource "helm_release" "argocd_devstg" {
count = var.enable_argocd_devstg ? 1 : 0
name = "argocd-devstg"
namespace = kubernetes_namespace.argocd_devstg[0].id
repository = "https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm"
chart = "argo-cd"
version = "6.7.3"
values = [
templatefile("chart-values/argocd.yaml", {
argoHost = "argocd-devstg.${local.environment}.${local.private_base_domain}"
ingressClass = local.private_ingress_class
clusterIssuer = local.clusterissuer_vistapath
roleArn = data.terraform_remote_state.eks-identities.outputs.argocd_devstg_role_arn
remoteServer = "remoteServer"
remoteName = "remoteName"
remoteClusterCertificate = "remoteClusterCertificate"
bearerToken = "bearerToken"
}),
# We are using a different approach here because it is very tricky to render
# properly the multi-line sshPrivateKey using 'templatefile' function
yamlencode({
configs = {
secret = {
argocd_devstgServerAdminPassword = data.sops_file.secrets.data["argocd_devstg.serverAdminPassword"]
}
# Grant Argocd_Devstg access to the infrastructure repo via private SSH key
repositories = {
webapp = {
name = "webapp"
project = "default"
sshPrivateKey = data.sops_file.secrets.data["argocd_devstg.webappRepoDeployKey"]
type = "git"
url = "git@github.com:VistaPath/webapp.git"
}
}
}
# Enable SSO via Github
server = {
config = {
url = "https://argocd_devstg.${local.environment}.${local.private_base_domain}"
"dex.config" = data.sops_file.secrets.data["argocd_devstg.dexConfig"]
}
}
})
]
}
Note these lines:
remoteServer = "remoteServer"
remoteName = "remoteName"
remoteClusterCertificate = "remoteClusterCertificate"
bearerToken = "bearerToken"
Dictionary:
- remoteServer: the target cluster API URL
- remoteName: the target server name (the ARN)
- remoteClusterCertificate: the target cluster CA Certificate on Base64
- bearerToken: the Token generated for the ServiceAccount
And this in the second file:
configs:
clusterCredentials:
- name: ${remoteName}
server: ${remoteServer}
labels: {}
annotations: {}
namespaces: namespace1,namespace2
clusterResources: false
config:
bearerToken: ${bearerToken}
tlsClientConfig:
insecure: false
caData: ${remoteClusterCertificate}
clusterResources false is so that ArgoCD is prevented to manage cluster level resources.
namespaces scopes the namespaces on which ArgoCD can deploy resources.
Apply the layer:
leverage tf apply
Info
This step will create the external-cluster configuration for ArgoCD.
Now you can see the cluster in the ArgoCD web UI.
Deploying stuff to the target cluster ¶
To deploy an App to a given cluster, these lines have to be added to the manifest:
spec:
destination:
server: "https://kubernetes.default.svc"
namespace: "appnamespace"
Being spec.destination.server here the config.clusterCredentials[*].server in the ArgoCD's external cluster secret.
Notes on multiple ArgoCD instances in the same cluster ¶
If multiple cluster wide ArgoCD instances will be deployed to the same cluster, this has to be kept in mind.
ArgoCD will pick up the ArgoCD Applications from the same namespace the ArgoCD instance is deployed in. (Unless it is set with additional namespaces)
Despite this, ArgoCD adds a label to know what ArgoCD Applications it has to manage. (It seems to be, at some point, ArgoCD will get all the ArgoCD Applications in the cluster and will filter them by label)
So, it is needed to set different labels to be used by each ArgoCD instance.
To do this, in the Helm configuration file in the components layer (for this example it is shared/us-east-1/k8s-eks/k8s-components), under directory chart-values, in the ArgoCD values file, add this:
configs:
cm:
application.instanceLabelKey: argocd.argoproj.io/instanceenv
Note if you already have the configs key, you must add the value the the current key, e.g. for the example above:
configs:
clusterCredentials:
- name: ${remoteName}
server: ${remoteServer}
labels: {}
annotations: {}
namespaces: namespace1,namespace2
clusterResources: false
config:
bearerToken: ${bearerToken}
tlsClientConfig:
insecure: false
caData: ${remoteClusterCertificate}
cm:
application.instanceLabelKey: argocd.argoproj.io/instanceenv
If the default labels are used by the two instances, they will try to manage the same ArgoCD Application (despite the fact they are in different namespaces), and they will conflict.